Due to the increasing shortage of industrial wood and also associated policy changes in recent years, agro-residues like bagasse has become an important raw material alternative to wood for panel products. Currently, bagasse is majorly used for power generation in sugar industry. However, as cost of electricity generation from renewable sources, is becoming more competitive, government may not offer lucrative rates for procuring additional power from sugar factories in future. In such case, excess bagasse can be utilized to manufacture particleboard, which is a substitute for plywood applications and is less costly compared to plywood.
Particleboard is a type of engineered wood and it is produced from wood particle, or fibre particles (like bagasse), which are glued together and pressed under high pressure and temperature to make it into a particleboard.
Around 3 decades ago, 3 sugar factories in India had set up particleboard manufacturing plants and these plants failed miserably because that time was not right to launch this product, as wood was available in abundance. Now, government of all countries have banned to cut trees in order to save the environment, in such case particleboard could be an alternative to plywood.
India currently imports particleboard worth $35 million, majorly from Thailand, Malaysia and Germany. There are around 46 particleboard manufacturing plants of capacity 100-280 CBM (m3) functioning in India, 27 of them are manufacturing wood base particleboard and 19 of them are bagasse based. Particleboard industry in India currently has turnover of Rs.8000 crores and is expected to grow 8-12% (CAGR) for the next 4-5 years.
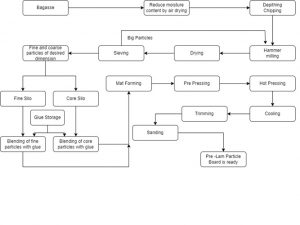
Process of manufacturing particleboard from bagasse
- The bagasse can be received either as baled bagasse or loose bagasse at Particle Board Plant. The baled bagasse is to be made loose bagasse in bale breaker and stored in Wet bagasse Silos. From Silos through conveyer, it is taken into bagasse hammer where it is broken down into smaller particles.
- The bagasse having 45-53% moisture is feed through conveyer at desired constant rate to dryer where it is dried to (2.2 to 5%) moisture. The bagasse is dried in dryer by using hot air which is produced in Hot Air Generator. In bagasse drier use hot air at temp 400°C-460°C which is obtained from Hot air Generator. And at the outlet of bagasse drier this temperature become 100°C.
- The dried bagasse is allowed to pass through screens to separate different size of components required for surface and core of board.
- The different size particles are stored in surface and core Silos.
- The oversized bagasse particles from screen are fed to the Hammer Mill to make small size components and used in the process again.
- The surface and core components are blended with desired Quantity of Glue i.e., Urea Formaldehyde. Blending for core is 8– 9% and for Fine surface 10-11% of urea formaldehyde with 52-55% of solid. Urea Formaldehyde available in India
- In Forming machine, the formation of thick blanket of matt start forming with components of bagasse suitable for surface and Core.
- The blanket so formed moved to pre-press with the help of conveyer where blanket thickness, weight and moisture are controlled before feeding to the Press.
- On the Prepress conveyer cross saw and edge trimmer are mounted which cut the mat to suitable length and trims the edges
- The waste material so obtained is recycled.
- The matt board from the prepress is fed to the Hydraulic Press with the help of loader. In Hydraulic press desired pressure and temperatures is approximately160°C and 180 kg/cm2. Pressure is maintained for proper thickness of the board for approximately 3 mins.
- The board so produced is moved to the star cooler with the help of Unloader and conveyer. The cycle time i.e., from loading to unloading is 5 min out of which board is pressed for 3 mins.
- The board cooled in star cooler to 45–50°C for 24 hrs. to ensure proper conditioning before giving finishing in Sanding Machine.
- Again, Board is trimmed to length & breadthwise as per the requirement. From star cooler boards so produced travels to sanding machine through conveyer for proper finish and smoothness of surface before that it’s excess length and breadth are cut to size automatically with the help of longitudinal and cross saws mounted at the appropriate places
- From sanding machines, the finished boards are moved to the storage area with help of fork lift.
- Size of the board i.e., 4 x 8 ft, 6 x 9 etc. can be decided on market requirement.
- In case we are using wood/wood chips/wheat stalk/ Rice husk – we use drum chipper/flaker instead of hammer will (as used in Bagasse) – while dryer onwards the process is same.
Process Diagram
Total bagasse required annually (330 days) for a 200 CBM particleboard manufacturing plant is 1,00,00 metric tons, project cost to set up the plant is Rs. 70 crores (excluding land cost) and payback period is around 3 years. Also, the value appreciation by converting bagasse into particleboard is 3 times.
Conclusion
Based on our experience of successfully commissioning more than 15+ particleboard/MDF (medium density fibre board) plants in India, we are certain that it is the correct time for Indian sugar factories to diversify into manufacturing of particleboard from bagasse, as the project offers attractive ROI (return on investment) and marketing assistance for 100% offtake of particleboard is also now available.
Disclaimer: The views and opinions expressed in the article by Pratik Vaydande, Senior Manager- Sugar Department at Protos Engineering Co. Pvt Limited are solely his own.















