India’s ethanol policy has transformed the sugar industry by promoting the production of ethanol from sugarcane juice and molasses. This change has not only provided a profitable alternative to the sugar mills but has also contributed to the country’s energy security and environmental sustainability. The success of this policy is evident in the increase in ethanol blend percentage from 1.6% in 2013-14 to 13% in 2023-24, with a target of 20% by 2025. The sugar industry in the country is the second largest agro-based industry after textiles.
5 crore sugarcane farmers (including family members) and 5 lakh direct workers are dependent on this industry. Apart from this, lakhs of people who are indirectly dependent are creating commercial and industrial opportunities. It is the second largest sugar producing country in the world.
Generally, 340 to 350 lakh tonnes of sugar is produced and up to 45 lakh tonnes of sugar is classified for ethanol production. Domestic consumption of 29 million tonnes of sugar is the highest in the world. The total annual turnover has gone up to Rs 2 lakh crores. The Ethanol Blending Program has saved the country a whopping amount in foreign exchange. The country needs 1000 crores liters of ethanol from the industry for 20% ethanol mixture, and if the ethanol required for other purposes is taken into consideration, the present production capacity is 875 crore liters, it has to be increased to 1350 crores litres.
BENEFITS TO THE SUGAR INDUSTRY –
1) Financial Stability: The policy has provided sugar mills with an additional revenue stream, reducing their dependence on sugar prices, which are often volatile.
2) Energy Security: By producing ethanol domestically, India has reduced its dependence on imported crude oil, thereby saving a large amount of foreign exchange.
3) Environmental Impact: Ethanol is a cleaner fuel compared to petrol, resulting in lower greenhouse gas emissions and a smaller carbon footprint.
4) Support to farmers: The policy ensures that sugarcane farmers have access to an assured market for their produce, leading to better income stability and timely payment.This comprehensive approach has made India a leader in ethanol production, benefiting the sugar industry and the wider economy.
OBJECTIVES: The Ethanol Blending Program (EBP) is an important initiative of the Government of India aimed at promoting the use of ethanol as a fuel additive in petrol. Here are some key aspects of the program:
1) Reduce dependence on fossil fuels: By blending ethanol into petrol, India aims to reduce its dependence on imported crude oil.
2) Environmental benefits: Ethanol is a cleaner-burning fuel, which helps reduce greenhouse gas emissions and improve air quality.
3) Support to the agricultural sector: The program provides a stable market to sugarcane farmers and helps manage surplus sugar production.
4) Blending targets: The EBP initially set a target of 5% ethanol blending with petrol, which has been progressively increased. The current target is to achieve a 20% ethanol blend by 2025.
Production Promotion: Government provides financial incentives and subsidies to sugar mills and distilleries to promote ethanol production.
5) Infrastructure Development: Investments are being made in infrastructure for ethanol production, storage and distribution.
ACHIEVEMENTS:
1) Increased blending rate: Ethanol blending rate has increased from around 1.6% in 2013-14 to more than 13% in recent years. The details of are as follows:
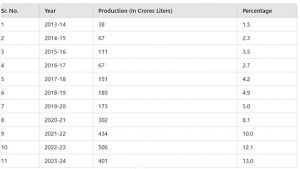
(Figures in crore litres; Supply years are Dec-Nov, Dec-Oct for 2022-23 and Nov-Oct for 2023-24: Nov-June)
ECONOMIC IMPACT: The program has provided additional revenue streams for sugar mills, helping them manage the cyclical nature of sugar prices.
1) Energy Security: By producing ethanol domestically, India has been able to save foreign exchange and reduce its energy import bill.
2) Feedstock availability: Ensuring a consistent supply of feedstock (sugarcane and other biomass) for ethanol production can be challenging.
Infrastructure: Developing the necessary infrastructure for large-scale ethanol production and distribution requires significant investment.
3) Policy Coordination: Effective coordination between various government departments and stakeholders is essential for the success of the programme.
The Ethanol Blending Program is a comprehensive approach to creating a sustainable and self-sufficient energy ecosystem in India.
GOVERNMENTS INCENTIVES TO SUGAR INDUSTRY:
The Government of India has implemented several incentives to promote ethanol production, especially from sugarcane. Here are some key solutions:
1) Financial incentives-
Subsidy: The government provides subsidies to sugar mills and distilleries for setting up ethanol production plants. This includes financial support for new projects and expansion of existing facilities.
Soft Loans: Loans are given to sugar mills at low interest rates for setting up ethanol production units. These loans often come with interest concessions (interest rate subsidies) to make them more affordable.
2) Price and purchase-
Remunerative price: The government has fixed a fixed, remunerative price for ethanol produced from various feedstocks such as sugarcane juice, B-heavy molasses and C-heavy molasses. This ensures that producers get a fair price for their ethanol2.
Guaranteed Offtake: Oil Marketing Companies (OMCs) are obliged to purchase ethanol from domestic producers at fixed prices, ensuring a stable market for ethanol 2 .
3) Policy support-
Ethanol Blending Targets: The government has set ambitious ethanol blending targets, aiming for 20% ethanol blending in petrol by 2025. This creates a steady demand for ethanol.
Infrastructure Development: Investments are being made in infrastructure for ethanol production, storage and distribution. This includes setting up ethanol production plants and increasing the capacity of existing plants.
4) Feedstock Diversification-
Alternative Foodstuffs: The government is promoting the use of alternative feedstocks such as maize and surplus rice for ethanol production. This helps in reducing the pressure on sugarcane and stabilizes the supply of raw material. These incentives are designed to make ethanol production economically viable and sustainable, benefiting both the sugar industry and the broader energy sector.
CHALLENGES BEFORE SUGAR INDUSTRY:
Despite the incentives given by the government, sugar mills face many challenges while adopting ethanol production. Here are some major obstacles:
1) Financial difficulties-
High initial investment: Setting up an ethanol production facility requires significant capital investment, which can be a barrier for many sugar mills, especially small ones.
Operational Expenses: The cost of maintaining and operating ethanol production units can be high, which affects overall profitability.
2) Feedstock availability-
Seasonal variability:The availability of sugarcane and other feedstocks can be seasonal, causing ethanol production capacity to fluctuate.
Competitive Usage: Sugarcane is also used for sugar production, and factories must balance the production of sugar and ethanol, especially when sugar prices are high.
3) Infrastructure and Logistics-
Storage and distribution: Adequate infrastructure is required to store and transport ethanol. Many regions lack the necessary facilities, making it difficult to increase production.
Supply Chain Management: Efficient supply chain management is critical to ensure a steady flow of raw materials and finished products. This can be challenging in areas with poor logistics infrastructure.
4) Regulatory and policy issues-
Policy Uncertainty: Frequent changes in government policies and regulations can create uncertainty, making it difficult for sugar mills to plan long-term investments.
Licensing and Approvals: Obtaining the necessary permits and approvals for ethanol production can be a time-consuming and bureaucratic process.
5) Technical challenges-
Adoption of Technology: Adoption of new technologies for ethanol production requires technical expertise and training, which may not be readily available.
Quality Control: Ensuring consistent ethanol quality to meet regulatory standards can be challenging, especially for mills new to ethanol production. Addressing these challenges requires coordinated efforts by governments, industry stakeholders and financial institutions to create a supportive ecosystem for ethanol production.
ROLE OF GOVT. TO SUPPORT INTEGRATED PRODUCTION OF SUGAR & ETHANOL:
Government policy plays an important role by creating an enabling environment for investment, innovation and sustainable practices for integrated production of sugar and ethanol. Here are some of the key ways government policy supports this integration:
1) Financial assistance and incentives-
Subsidies and Grants: The government provides grants and subsidies to sugar mills for setting up and expanding ethanol production facilities. This financial support reduces the initial investment burden and encourages mills to diversify their operations.
Soft Loan and Interest Subsidy: Low interest loans and interest concession schemes make it easier for sugar mills to access capital needed to upgrade their infrastructure and adopt new technologies.
2) Regulatory Framework-
Ethanol Blending Mandates: The government has set mandatory ethanol blending targets, such as achieving the current target of 20% ethanol blending in petrol by 2025. These mandates create a steady demand for ethanol, which encourages mills to invest in production.
Simplified Licensing and Approvals: Simplifying the process for obtaining licenses and approvals for ethanol production helps reduce bureaucratic delays and facilitates faster project implementation.
3) Beneficial Price: The government sets fixed, remunerative prices for ethanol produced from various feedstocks, ensuring that producers get a fair return on their investment.
4) Guaranteed Offtake Agreements: Oil Marketing Companies (OMCs) are obliged to purchase ethanol from domestic producers at fixed prices, providing a guaranteed market for ethanol and reducing market risk for producers.
5) Infrastructure development – The government invests in developing the necessary infrastructure for ethanol production, storage and distribution. This includes setting up ethanol production plants and increasing the capacity of existing projects.
6) Logistics Support: Improving logistics and transport infrastructure ensures efficient movement of raw materials and finished products, reducing operational bottlenecks.
7) Research and Development-
Funding for R&D: The government allocates funds for research and development in ethanol production technology, which helps improve efficiency and reduce costs.
Collaboration with Research Institutes: Encouraging collaboration between sugar millers, research institutes and universities promotes innovation and adoption of best practices in integrated production.
8) Environment and Sustainability Policies – Implementation and enforcement of environmental regulations ensures that ethanol production processes are sustainable and have minimal negative impact on the environment.
9) Support for sustainable practices- Policies that promote the use of alternative feedstocks and by-products, such as bagasse for co-production, help create more sustainable production ecosystems.
Government policies play an important role in enabling sugar mills to optimize their operations for both sugar and ethanol production, by providing financial incentives, creating a supportive regulatory framework and investing in infrastructure and research.
OVERALL BENEFITS OF ETHANOL POLICY TO SUGAR INDUSTRY:
The ethanol policy of the Government of India has brought many significant benefits to the sugar industry. Here are the main benefits:
1) Financial benefits-
Additional revenue streams: Ethanol production provides sugar mills with an alternative source of income, reducing their dependence on the often volatile sugar market.
Price Stability: By diversifying their product portfolio, sugar millers can better manage price fluctuations in the sugar market, leading to more stable financial performance.
2) Support to farmers-
Guarantee Market: This policy ensures steady demand for sugarcane, providing farmers with a reliable market for their produce.
Timely Payment: With the additional revenue from ethanol, sugar mills are in a better position to make timely payments to farmers, improving their financial stability.
3) Energy security –
Decrease in oil import: By increasing domestic ethanol production, India can reduce its dependence on imported crude oil, enhancing national energy security.
4) Foreign Exchange Savings: Less import of oil leads to significant savings in foreign exchange, which benefits the overall economy.
5) Environmental benefits-
Low emissions: Ethanol is a cleaner-burning fuel than gasoline, which reduces greenhouse gas emissions and improves air quality.
Sustainable Conduct: The policy encourages the use of alternative feedstocks and byproducts, promoting more sustainable agricultural and industrial practices.
6) Infrastructure development-
Investment in Facilities: The policy has encouraged investment in ethanol production facilities, job creation and boosting the local economy.
Enhanced Logistics: Improved infrastructure for ethanol storage and distribution benefits the entire supply chain from farmers to end consumers.
7) Technological progress-
Innovation: The push for ethanol production has led to technological advances in distillation and fermentation processes, increasing efficiency and reducing costs.
Research and Development: A focus on R&D has led to better utilization of feedstock and byproducts, further enhancing the sustainability of the sugar industry.
Overall, the government’s ethanol policy has provided a comprehensive framework to support the sugar industry economically, environmentally and technologically. This integrated approach not only benefits the industry but also contributes to the broader goals of energy security and environmental sustainability. Ultimately, India’s ethanol policy is a transformative force for the sugar industry, providing financial stability, supporting farmers and contributing to national energy security. By promoting ethanol production, the government has created a sustainable revenue stream for sugar mills, reducing their dependence on volatile sugar prices. The policy’s environmental benefits, by reducing greenhouse gas emissions and promoting sustainable practices, further underline its importance. As India moves towards its ambitious ethanol blend target, synergies between the sugar and energy sectors promise a more resilient and sustainable future for the country.
P.G. Medhe is the former Managing Director of Shri Chhatrapati Rajaram Sahakari Sakhar Karkhana Ltd and sugar industry analyst. He can be contacted at +91 9822329898.












