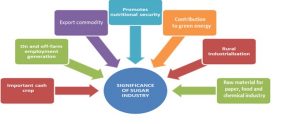
With over 450 million metric tonnes of sugarcane production, approx. 5.5 million hectares of land under sugarcane cultivation, 50 million sugarcane farmers, +33 million metric tonnes of sugar production per annum and being significant contributor green energy, Indian sugar industry is considered as the backbone of the rural economy in the country.The relationship between the sugar industry in India and rural development in India is a symbiotic one, where the growth and development of one positively impacts the other. The sugar industry provides enormous opportunities for developing “Entrepreneurship” and “Start Ups” to exploit unharnessed potential of sugarcane value chain thus helping in enhancing viability of sugar units and strengthening the rural economy, said Prof. Narendra Mohan, Former Director, National Sugar Institute, Kanpur.
Although, generating more revenue streams through Innovations and diversification to produce more value-added products viz. power, ethanol and compresses bio-gas over the last few years has helped the Indian sugar industry to have a better economic sustainability as compared to being a stand-alone sugar factory, but still there is a long way to go. Capacity building which took place for production of ethanol and compressed bio-gas and expansion in crushing capacities by the sugar factories has brought new investments, job opportunities and strengthening of rural economy over the last few years.
Ethanol industry, in particular, has grown by leaps and bounds over the last couple of years with more and more units being coming up. In pursuit of converting “waste to resource” in ethanol units, while the recovery of CO2 from the fermenters has gained momentum for use in fertilizer and beverage industry or as “dry ice”, the spent wash generated in molasses based distilleries has become the centre of attraction for the available potash content. The ash from the incineration boilers after addition of binders and micro-nutrients has been successfully granulated as potash rich fertilizer.
However, the sugarcane crop and sugar industry can provide ample opportunities to further diversify and produce value added products utilizing sugarcane, its products, by-products and waste in an innovative manner and in fact a “Bio-refinery” model appears to be the future of the Indian sugar industry to be sustainable.
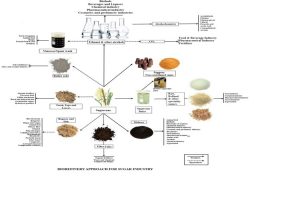
A cohesive effort towards sustainable waste management, value-addition and utilization of by-products in an innovative manner may further improve the economic sustainability of the sugar industry benefitting all stakeholders including farmers. Since the sugar industry, as observed, may not be very keen to take up smaller projects for production of bio-products, bio-food and bio-chemicals etc., the need of the hour is to develop “Entrepreneurship” and “Start Ups” for taking this philosophy forward resulting in overall development of the rural areas bringing new investments, job opportunities and providing environment friendly solutions to various requirements of the society opined Prof. Mohan.












